Fines under theGeneral Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). What you need to know about GDPR fines, the guidelines on the application of GDPR administrative fines, ways to protect against GDPR fines, penalties, sanctions and the sanction mechanism under the GDPR.
If there is one thing that people know about the GDPR it’s that GDPR fines (administrative fines) can go up to 20 million Euros or 4 percent of annual global (note global!) turnover, whichever of both is highest.
Territorial Scope (<--- Link to the gdpreu.org source)
| Despite being a European Union regulation, the GDPR has far-reaching implications for any business that has a global presence. In short, it impacts any business, EU-based or not, that has EU users or customers. This represents a key change relative to the current Directive. |
(Click image to view source page)
Fines and Penalties (<--- Link to the gdpreu.org source)
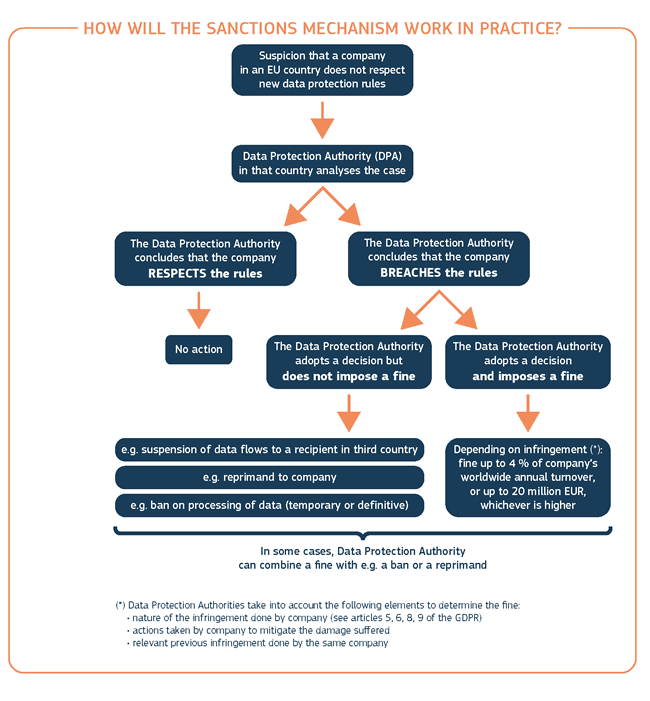
Administrative finesThe GDPR imposes stiff fines on data controllers and processors for non-compliance. DeterminationFines are administered by individual member state supervisory authorities (83.1). The following 10 criteria are to be used to determine the amount of the fine on a non-compliant firm:
AmountIf a firm infringes on multiple provisions of the GDPR, it shall be fined according to the gravest infringement, as opposed to being separately penalized for each provision. (83.3) However, the above may not offer much relief considering the amount of fines possible: Lower levelUp to €10 million, or 2% of the worldwide annual revenue of the prior financial year, whichever is higher, shall be issued for infringements of:
Upper levelUp to €20 million, or 4% of the worldwide annual revenue of the prior financial year, whichever is higher, shall be issued for infringements of:
|
Digital Data System Guards and Controls |